Operator:
A symbol that represents specific action.
Operand:
On which action is to be performed.
What is operator and operand:
For example 1+2.
Here 1 and 2 are operands.
+ symbol is operator.
Types of operators:
Precedence:
Operations need to be performed in an expression.
Invention:
Brian Huffine.
Also known as:
Order of operations.
Operator precedence parser:
Bottom up parser that interprets operator precedence grammar.
Bottom up parser:
Tree starting from bottom left end and incrementally works its way upwards and rightwards.
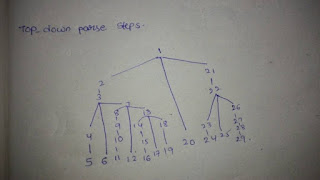
Top-down parser:
Hierarchial tree starting from top and incrementally works its way downwards and right wards.
Hierarchial:
Items are ranked according to the level of importance.
Operator precedence grammar:
Context free grammar.
Allow precedence in between the terminals of the grammar.
Precedence order:
Operator with the higher precedence goes first.
Precedence table:
Example:
Associativity:
When two operators with same precedence evaluated according to its associativity.
Types:
Left-associative:
Operations are grouped from left to right.
Right-associative:
Operations are grouped from right to left.
Advantages:
Simple to implement.
Can parse ambiguous grammar.
Brackets increase the readability of the code.
Ambiguous:
Some grammars allow more than one parse tree for same token.
Disadvantages:
Applicable for small class of grammars.
Cannot handle unary minus.
Difficult to decide which grammar is recognized by grammar.
Not sure that it accepts exactly the designed language.