Resolution:
Maximum size at which image can be printed while retaining quantity.
Number of pixels contained on a display monitor horizontally or vertically.
How resolution is measured:
Camera resolution is measured in Megapixels (Millions of pixels).
Image file and monitor resolution is measured in ppi.
Pixel:
Maximum size at which image can be printed while retaining quantity.
Number of pixels contained on a display monitor horizontally or vertically.
How resolution is measured:
Camera resolution is measured in Megapixels (Millions of pixels).
Image file and monitor resolution is measured in ppi.
Pixel:
Basic programmable color on computer display or in computer image.
Intensity of pixel:
Variable.
Intensity:
Power trasferred per unit area.
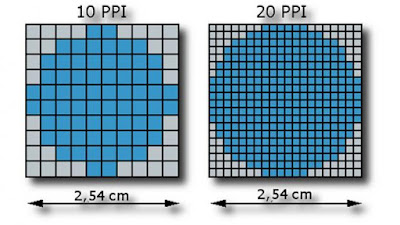
PPI:
Pixels Per Inch is a measure of the sharpness on the display screen.
Purpose:
Image will appear sharper.
Focus light will be maximum.
Design, plan.
Functional diagrams of resolution:

How do i get sufficient resolution:
Need 2 megapixel camera to set the highest resolution.
How does cropping effect resolution:
Reduce the number of pixels in the final image.
300 ppi image to 150 ppi image.
Conversion of low to high resolution images:
Using Photoshop.
Types of resolution:
Ordinary resolution:
Votes cast in favour of resolution exceeds the votes cast against it.
Simple majority is required to move the resolution.
Special resolution:
Votes cast in favour of resolution must be three times higher than the votes cast against it.
Majority of not less than 75% of those voting.
Screen resolution:
Clarity of text and images displayed on screen.
Items appear sharper.
How to change screen resolution in our system:
Low resolution:
known as lo-res.
small amount of pixels cause small and jaggy.
Advantages:
Memory is less.
No need to be resized.
Files are smaller in size.
Disadvantages:
Camera does not contain high pixels.
Crop an image will loose resolution.
High resolution:
Showing large amount of detail.
Advantages:
Clarity of image is good.
Disadvantages:
Need more memory for storing image.
Applications:
Used in profile websites.
Pharmaceuticals.
Supra molecular structures.
Polymers.
Inorganic–organic hybrids.
Intensity of pixel:
Variable.
Intensity:
Power trasferred per unit area.
PPI:
Pixels Per Inch is a measure of the sharpness on the display screen.

Purpose:
Image will appear sharper.
Focus light will be maximum.
Design, plan.
Functional diagrams of resolution:

How do i get sufficient resolution:
Need 2 megapixel camera to set the highest resolution.
How does cropping effect resolution:
Reduce the number of pixels in the final image.
300 ppi image to 150 ppi image.
Conversion of low to high resolution images:
Using Photoshop.
Types of resolution:
Ordinary resolution:
Votes cast in favour of resolution exceeds the votes cast against it.
Simple majority is required to move the resolution.
Special resolution:
Votes cast in favour of resolution must be three times higher than the votes cast against it.
Majority of not less than 75% of those voting.
Screen resolution:
Clarity of text and images displayed on screen.
Items appear sharper.
How to change screen resolution in our system:
known as lo-res.
small amount of pixels cause small and jaggy.
Advantages:
Memory is less.
No need to be resized.
Files are smaller in size.
Disadvantages:
Camera does not contain high pixels.
Crop an image will loose resolution.
High resolution:
Showing large amount of detail.
Advantages:
Clarity of image is good.
Disadvantages:
Need more memory for storing image.
Used in profile websites.
Pharmaceuticals.
Supra molecular structures.
Polymers.
Inorganic–organic hybrids.






