C++ programming language was developed in 1980 by Bjarne Stroustrup at bell laboratories of AT&T.
History:
| Language | Year | Developed By |
|---|---|---|
| Algol | 1960 | International Group |
| BCPL | 1967 | Martin Richard |
| B | 1970 | Ken Thompson |
| Traditional C | 1972 | Dennis Ritchie |
| K & R C | 1978 | Kernighan & Dennis Ritchie |
| C++ | 1980 | Bjarne Stroustrup |
Downloading C++:
Turbo C++ is used to write both C and C++ programs.
While writing C++ program we can see with .cpp extension for C++ programs.
Installing TurboC++:
Hello C++ program:
iostream ---- standard input output functions.
Provides cin and cout methods for reading from input and writing to output respectively.
#include ---- includes console input output library functions.
void main() ---- Entry point for every program. Specifies that it returns no value.
cout ---- Used to print the data on the console.
getch() ---- Asks for a single character. Until press any key blocks the screen.
Compile and run the program using shortcut key:
Press ctrl+F9 keys to compile and run the program directly.
Alt+F5 to view user screen any time.
Press Esc to return to turbo C++ console.
Output operation:
Bytes flow from main memory to device like printer, display screen, or a network connection is called output operations.
Input operation:
Bytes flow from device like printer, display screen, or a network connection to main memory is called input operations.
Standard output stream (cout):
Standard output device, which is usually a display screen.
Displays the output on the console.
Eg:
Output:
Value of ary is: Welcome to C++
Standard input stream (cin):
Standard input device, which is usually a keyboard.
Read the input from the console.
Eg:
Output:
Enter your age: 22
Your age is: 22
Standard endline (endl):
Used to insert a new line characters and flushes the stream.
Eg:
Output:
hi moulica
how are you
Variable:
Name of memory location.
Used to store data.
Syntax:
type variable_list;
Eg:
int x;
Syntax for variable initialization:
data_type variable_name = constant
Eg:
int a = 10;
Data Types:
| Data Types | Memory Size | Range |
|---|---|---|
| char | 1 byte | -128 to 127 |
| signed char | 1 byte | -128 to 127 |
| unsigned char | 1 byte | 0 to 127 |
| short | 2 byte | -32,768 to 32,767 |
| signed short | 2 byte | -32,768 to 32,767 |
| unsigned short | 2 byte | 0 to 32,767 |
| int | 2 byte | -32,768 to 32,767 |
| signed int | 2 byte | -32,768 to 32,767 |
| unsigned int | 2 byte | 0 to 32,767 |
| short int | 2 byte | -32,768 to 32,767 |
| signed short int | 2 byte | -32,768 to 32,767 |
| unsigned short int | 2 byte | 0 to 32,767 |
| long int | 4 byte | |
| signed long int | 4 byte | |
| unsigned long int | 4 byte | |
| float | 4 byte | |
| double | 8 byte | |
| long double | 10 byte |
Loops:
Iterate a part of program several times.
for loop:
Number of iterations is fixed can use for loop.
Syntax:
for(initialization; condition; increment / decrement) {
//code to be executed
}
Flow chart:
While loop:
Iterate a part of program several times.
Number of iterations is not fixed.
Syntax:
while(condition) {
//code to be executed
}
Flow chart:
Do-while loop:
Iterate a part of program several times.
Number of iterations is not fixed must have to execute the loop atleast once.
Condition is checked after loop body.
Syntax:
do {
//code to be executed
}while(condition);
Flow chart:
Control statements:
if statement:
Tests the condition. Executes if the condition is true.
Syntax:
if(condition) {
//code to be executed
}
Flow chart:
if-else statement:
Executes if block if condition is true otherwise else block will execute.
Syntax:
if(condition) {
//code to be execute if condition is true
} else {
//code if condition is false
}
Flow chart:
if-else-if ladder:
Executes one condition from multiple statements.
Syntax:
if(condition1) {
//code to be execute if condition1 is true
} elseif(condition2) {
//code to be execute if condition2 is true
} elseif(condition3) {
//code to be execute if condition3 is true
....
else {
//code to be executed if all conditions are false
}
Flow chart:
Switch:
Executes one statement from multiple conditions.
Like if-else-if ladder.
Syntax:
switch(expression)
case value1:
//code to be execute
break;
case value2:
//code to be execute
break;
....
default
//code to be execute if all conditions are not matched;
break;
}
Flowchart:
Break:
Breaks the current flow of the program.
Syntax:
jump-statement
break;
Flow chart:
Continue:
Continues the current flow of the program and skips the remaining code at the specified locations.
Syntax:
jump-statement;
continue;
Flow chart:
Goto:
Known as jump statement.
Transfers control to other part of the program.
Add two strings:
Find starting point for a string:
Read from user input and write to user output:
Read from a file:
Create an .txt file with some data in it.
Copy the .txt file in turboc3--Bin folder.
We can see the filename.txt folder in our bin folder.
After writing a program we can see the output what we have written in our .txt file.
Write to a file:
Then entering few lines of data to file.
Now, it will create a .txt file and data will be saved in it.
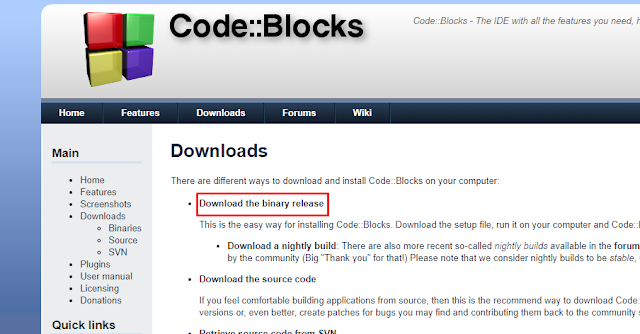
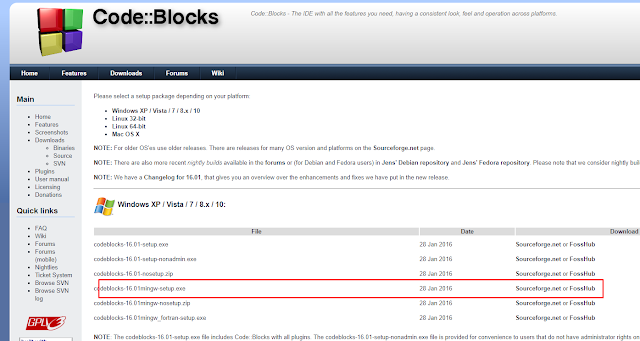
Downloading codeblocks:
Partial string:
Second and fourth line in a file:
Non repeated character in a string:
Permutation of a string:
Digit identification is string have any numbers:
Replacing first highest repeated character with user given character:
Pattern:
Database:




































































